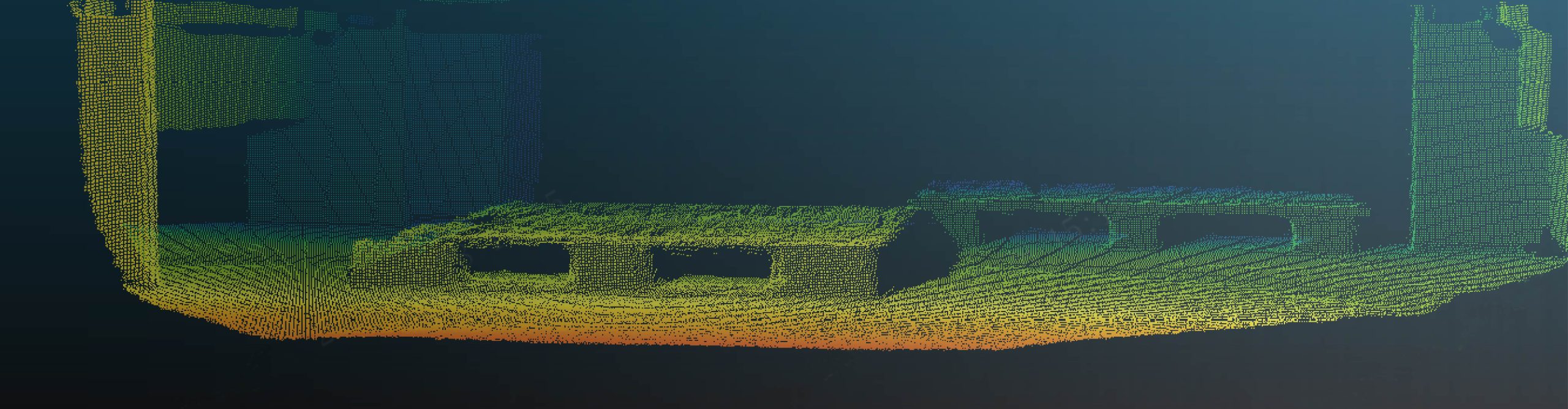

3D ToF Technology
Do a deep dive into various camera technologies and understand how they enhance the performance of camera-based devices and help machines see better.
-

A Game Changer in Automation? What is an RGB-D Camera?
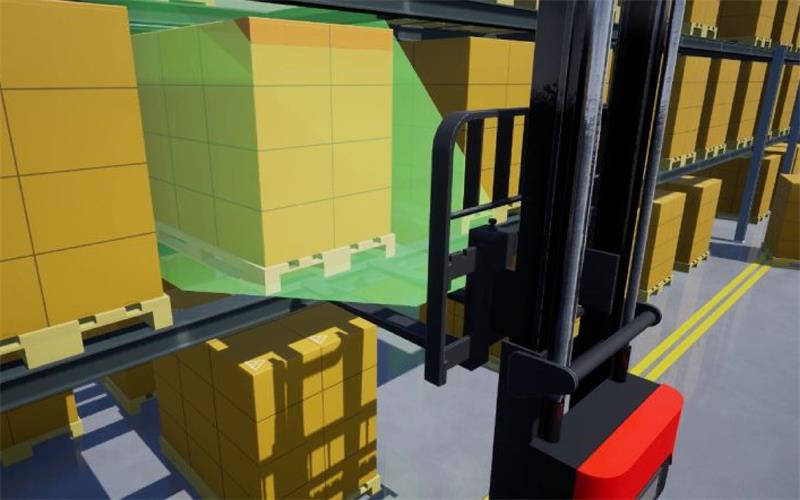
When an autonomous forklift precisely lifts a barcode-l […]
-

Optimizing Time-of-Flight (ToF) Camera Performance vs. Cost: Key Techniques for 3D Sensing Applications
In the era of rapid advancement in Industry 4.0 and sma […]
-
TN20-Structured Light vs. iToF: Technical deep comparison into active 3D sensing methods
This article primarily presents a performance comparison between structured light technology and iToF, and explores suitable application scenarios to help users select the appropriate camera based on their specific needs.
-
TN19-LiDAR vs. iToF: A comprehensive comparison in 3D technologies
This article introduces a comparison of the performance between LiDAR and iToF cameras, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages as well as their application scenarios, to help users select the appropriate camera based on their needs.
-

TN18-Introduction to the WDR function in Indirect Time-of-Flight (iToF) technology
This article introduces the WDR function, compared to regular images, can provide a wider detection range and more data detail. By utilizing the best detail images for each detection range, the final WDR image can achieve optimal imaging for both near and far scenes.
-
TN17-The Advantages of Time-of-Flight Cameras You Didn’t Know
Overview 3D cameras create a window into the real world […]
-
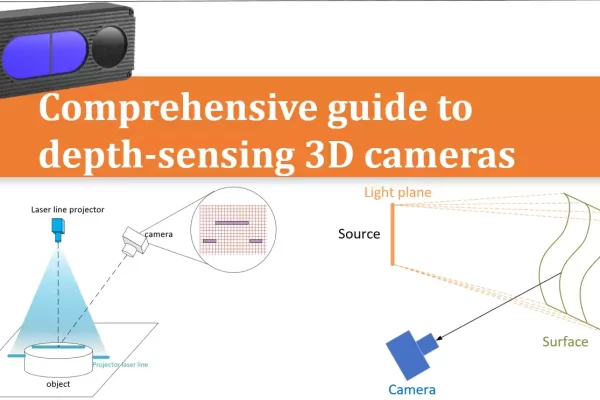
TN16-Comprehensive guide to depth-sensing 3D cameras technology
This article introduces the commonly used technical principles of current depth sensing cameras, analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of different types of cameras, and helps users better choose the products they need.
-
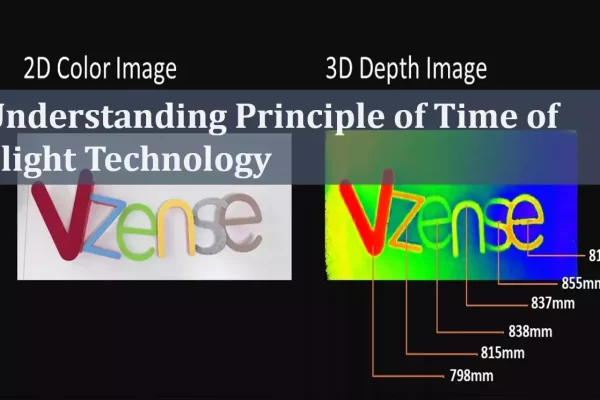
TN15-Understanding Principle of Time of Flight Technology
This article introduces the classification and principles of 3D ToF cameras, comparing their pros and cons. It provides a detailed description of the camera’s composition, helping users to better understand ToF cameras.
-

TN14-Understanding flying pixel filter and how it works
Flying points appear at depth discontinuities in the scene, especially at object boundaries, producing erroneous depth values, resulting in ghost pixels. This article introduces a filtering method to eliminate flying points.
-
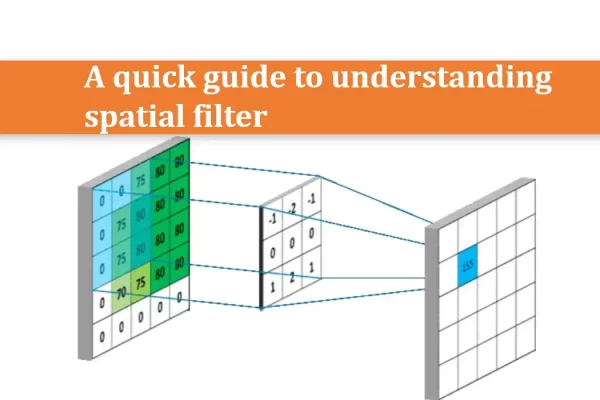
TN13-A quick guide to understanding spatial filter
This article introduces a noise-reducing filter—a spatial filter, achieving an overall smoothing effect. It also discusses the application and parameter settings of spatial filtering in ScepterGUITool, allowing users to intuitively perceive the effect of this filter.
-
TN12-A deep learning into confidence filter
This article introduces a filter for weak signal quality—confidence filtering. Confidence filtering is a high-pass filter. The higher the confidence value, the more reliable the data. For ToF cameras, it can be used to filter out objects with low reflectivity.
-

TN11-Understanding stray light: How to minimize the influence of it?
Stray light refers to the light from external sources that enters the lens and interacts with internal components. This article explains what stray light is, its sources, and how to reduce its impact on image quality.
-

TN10-A comprehensive guide to time filter
This article introduces time filtering used for smoothing noise and reducing image jitter. This filter is not suitable for moving scenes as it may cause motion blur. It also discusses the application and parameter settings of time filtering in ScepterGUITool.
-
TN09-Learning about Field of View (FoV)
This article introduces the coverage range of different fields of view for ToF cameras and the X and Y resolutions, helping users understand the resolution size of the measured objects in the ToF camera.
-
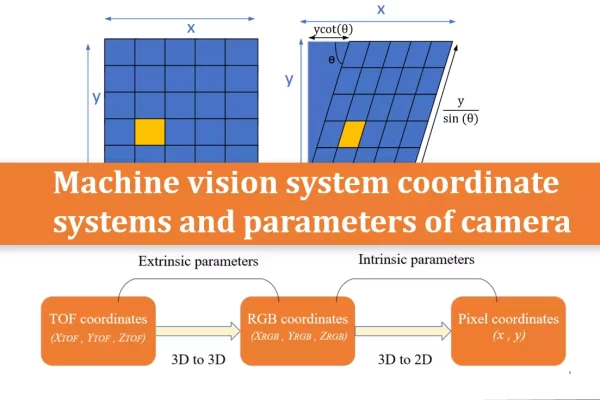
TN08-Machine vision system coordinate systems and parameters of camera
This article introduces the transformations between these three coordinate systems, how to obtain the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of the camera, and how to convert them into point clouds.
-

TN07-A deep diving into gamma gain of IR image of indirect Time-of-Flight (iToF)
Because the human eye perceives images as a logarithmic function of light intensity, there is a discrepancy between the device display and human perception of the image. This article introduces methods for compensating for this difference: gain and gamma correction.
-
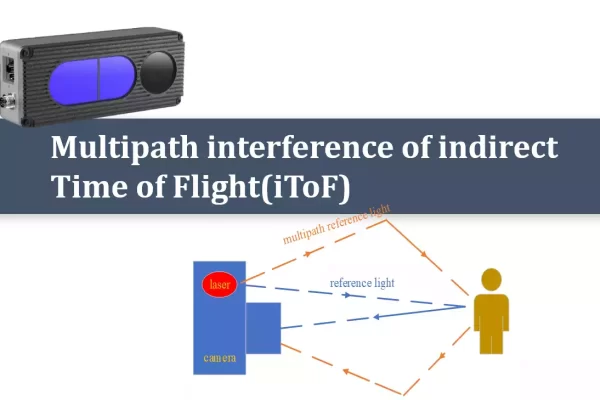
TN06-Multipath interference of indirect Time of Flight (iToF)
During the light reception, the light source received by a single pixel caused by one or multiple paths, which can lead to depth errors. This article provides a detailed introduction to scenarios that cause multipath interference and how to maximize the reduction of its impact.
-
TN05-Understanding High Dynamic Range (HDR) mode of indirect Time-of-Flight (iToF)
To handle the imaging issues caused by the coexistence of high and low reflectivity objects in the target area, this article introduces an HDR technology that can improve the situation.
-
TN04-What is the dual-frequency modulation of Continuous Wave indirect Time of Flight (CW-iToF)?
This article introduces a method to solve the CW-iToF rang aliasing phenomenon called dual-frequency measurement. This involves using two different frequencies on the same measurement object and determining the true distance from the results of the two measurements.
-
TN03-A quick guide to understanding range aliasing of Continuous Wave indirect Time of Flight (CW-iToF)
This article introduces a phenomenon called range aliasing. When the modulated light of the second cycle is emitted and detected before the first cycle returns , the sensor cannot distinguish which cycle’s modulated light is received, resulting in range aliasing phenomenon.
-

TN02-Introduction to the indirect Time of Flight(iToF) principle:Continuous Wave-iToF vs. Pulse-iToF
The working principle of iToF is that the camera itself emit modulated infrared light, the sensor receives the light signals returned from the measurement object. This article introduces two technological principles of iToF—Continuous Wave technology and Pulse technology.
-

TN01-Understanding accuracy vs. precision : What are their differences?
This article introduces the concepts of accuracy and precision. Accuracy is the standard for evaluating the deviation between measured values and true values. Precision is the standard for evaluating the performance between different measured values.
-

A Quick Understanding about 3D ToF Camera
In the realm of imaging technology, Time-of-Flight […]