Table of Contents
Technical principles
1. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
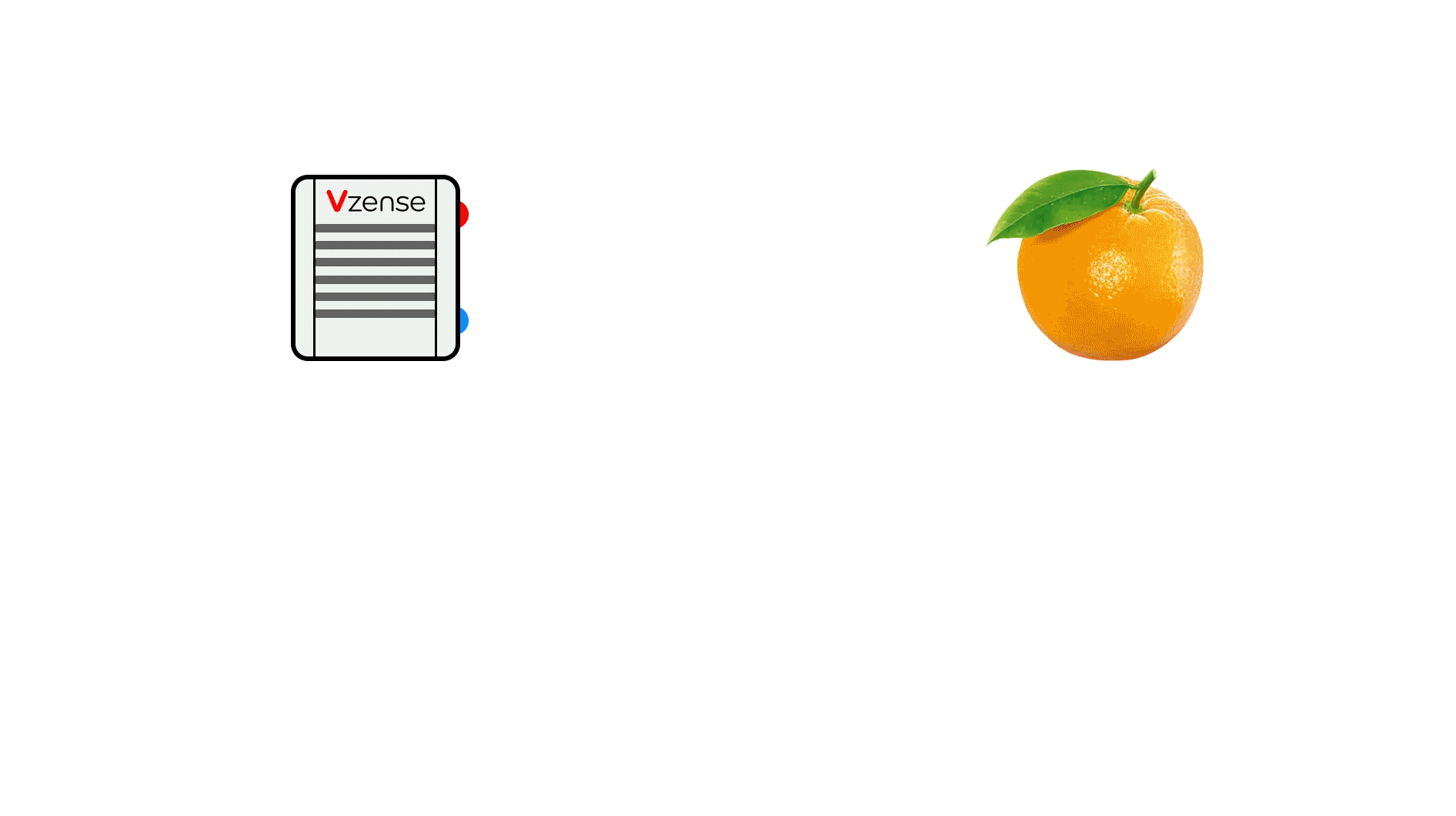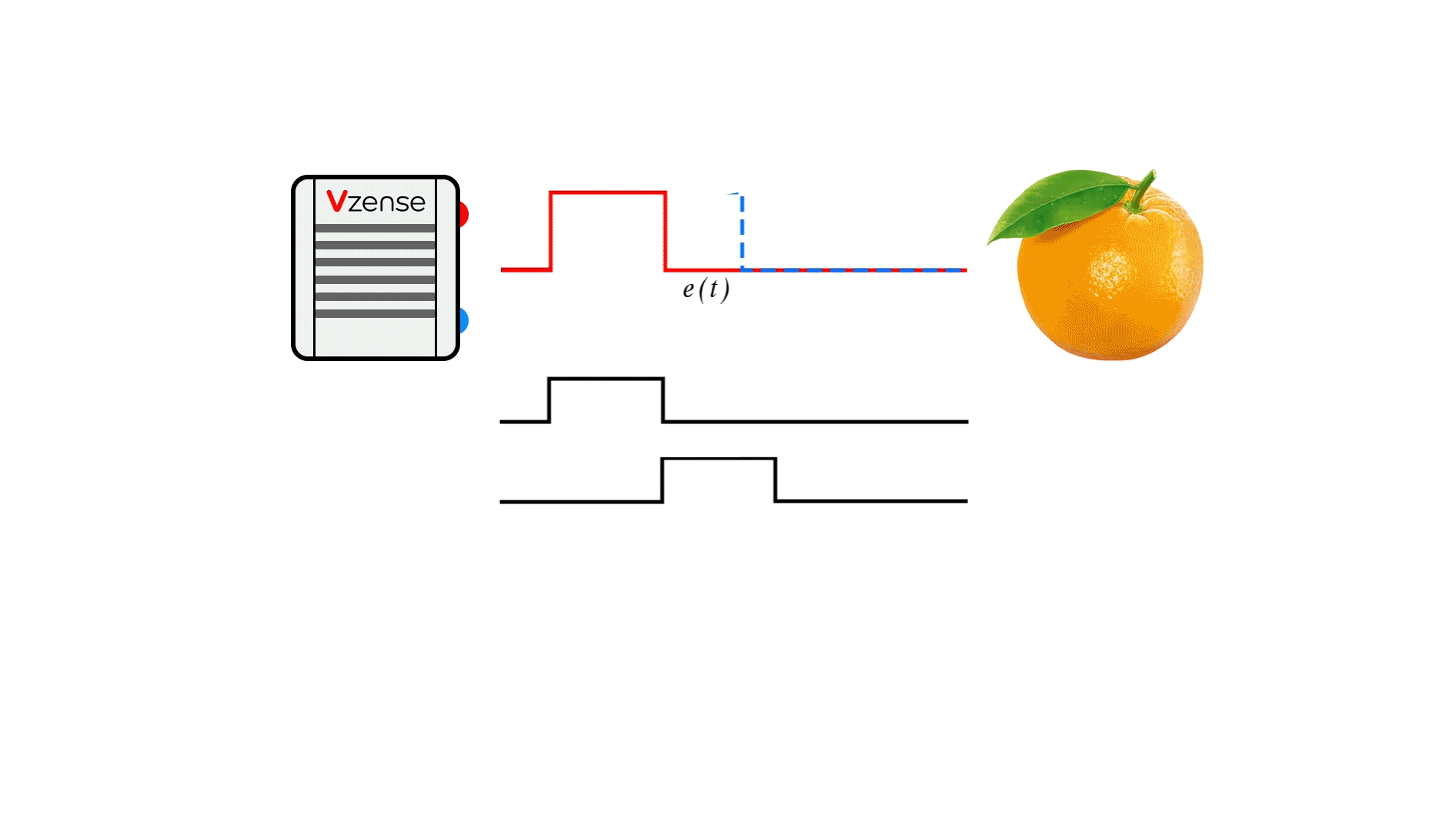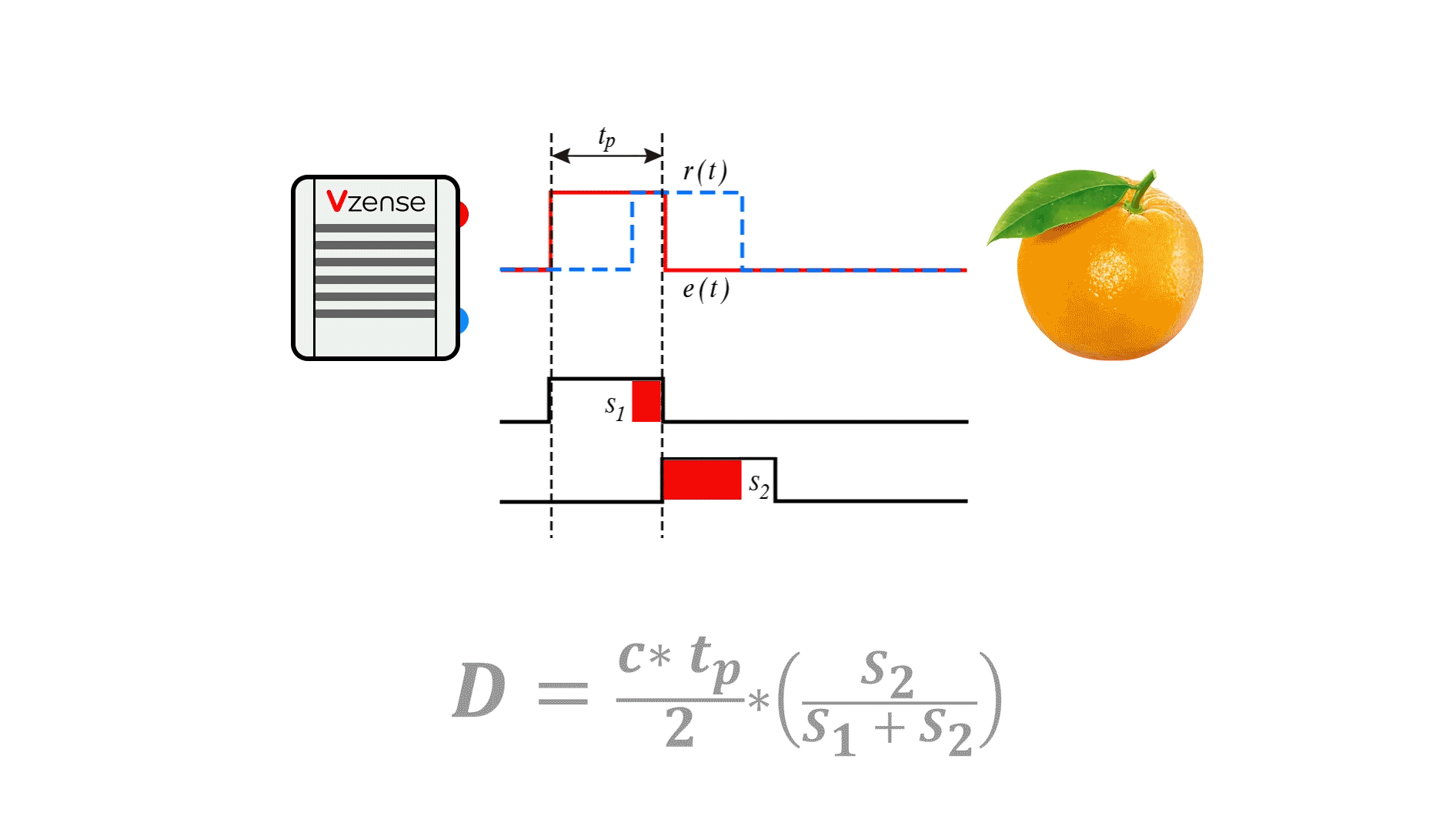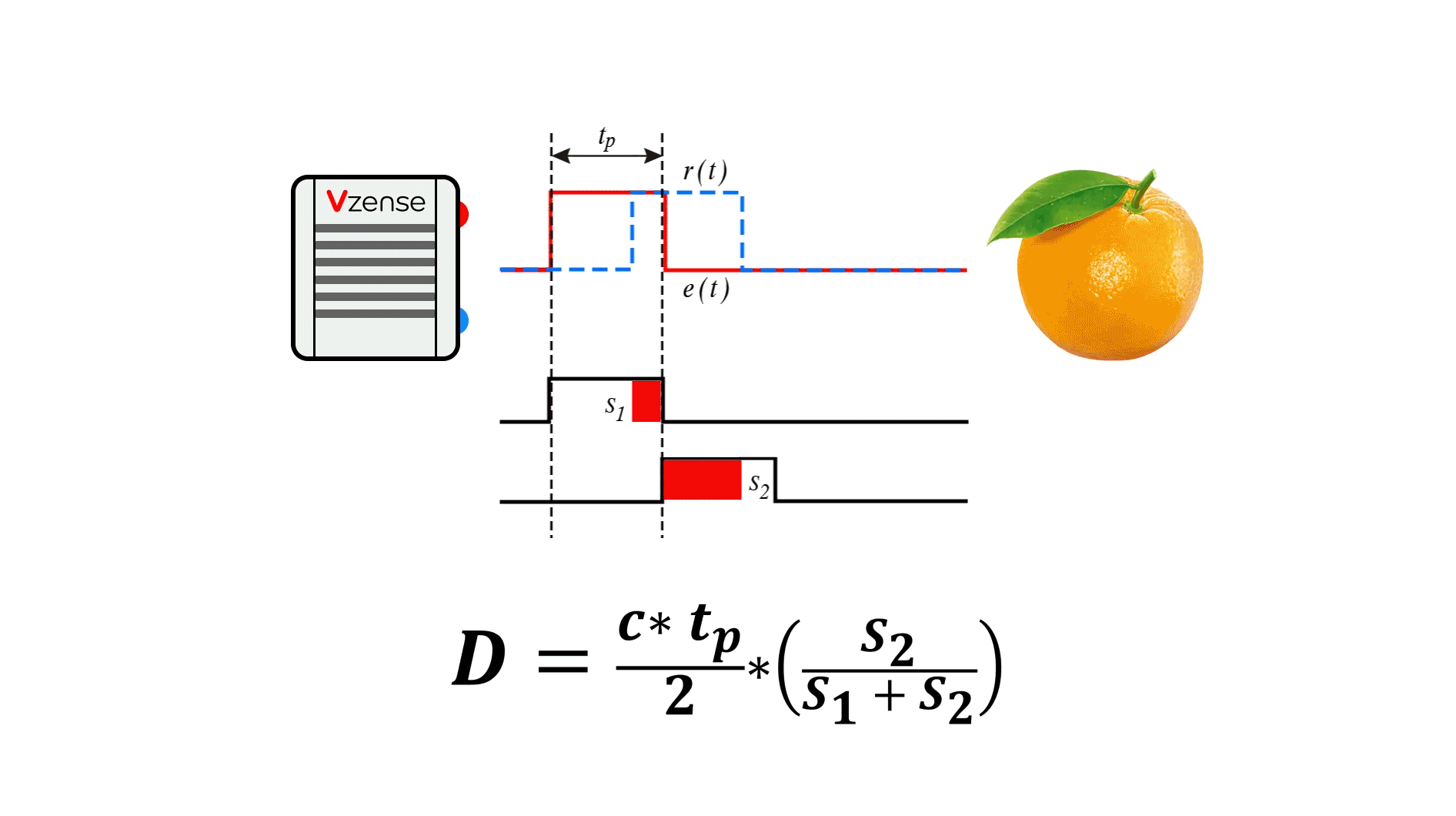
Principle: It calculates distances by emitting laser pulses and measuring the time taken for them to reflect back from a target, as shown in the table below.
Types: Triangulation method, direct Time-of-Flight (dToF), and Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW).
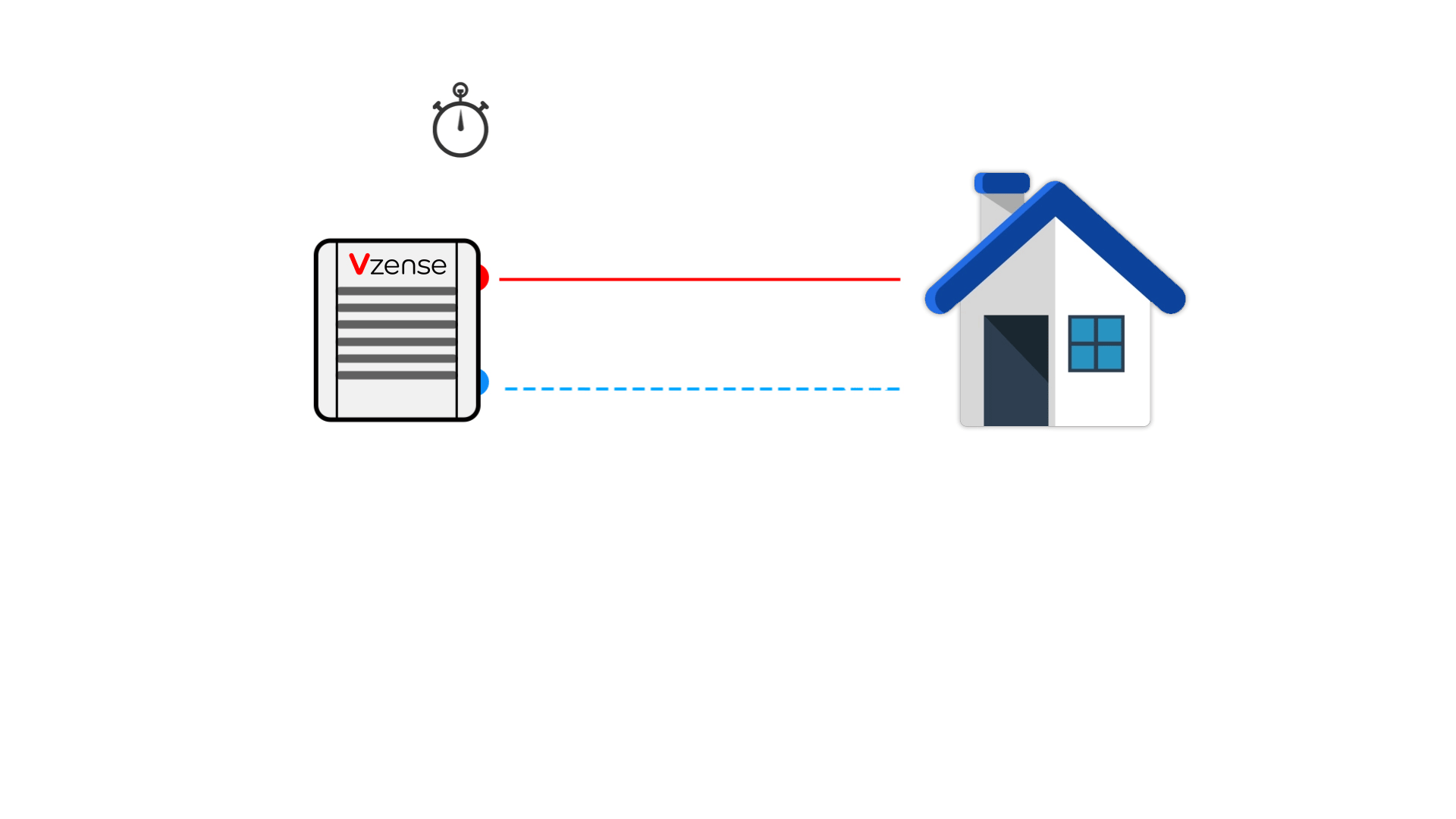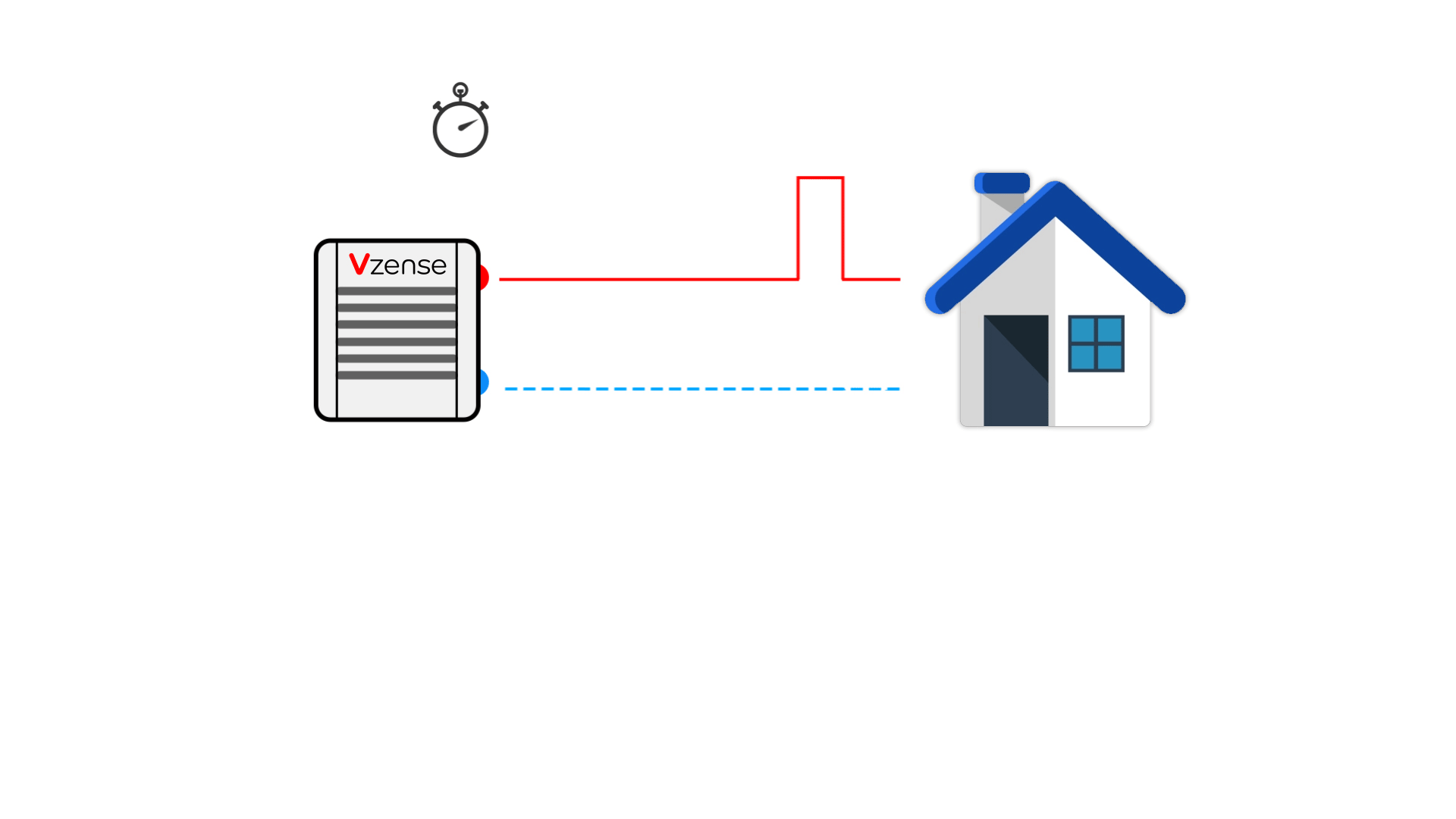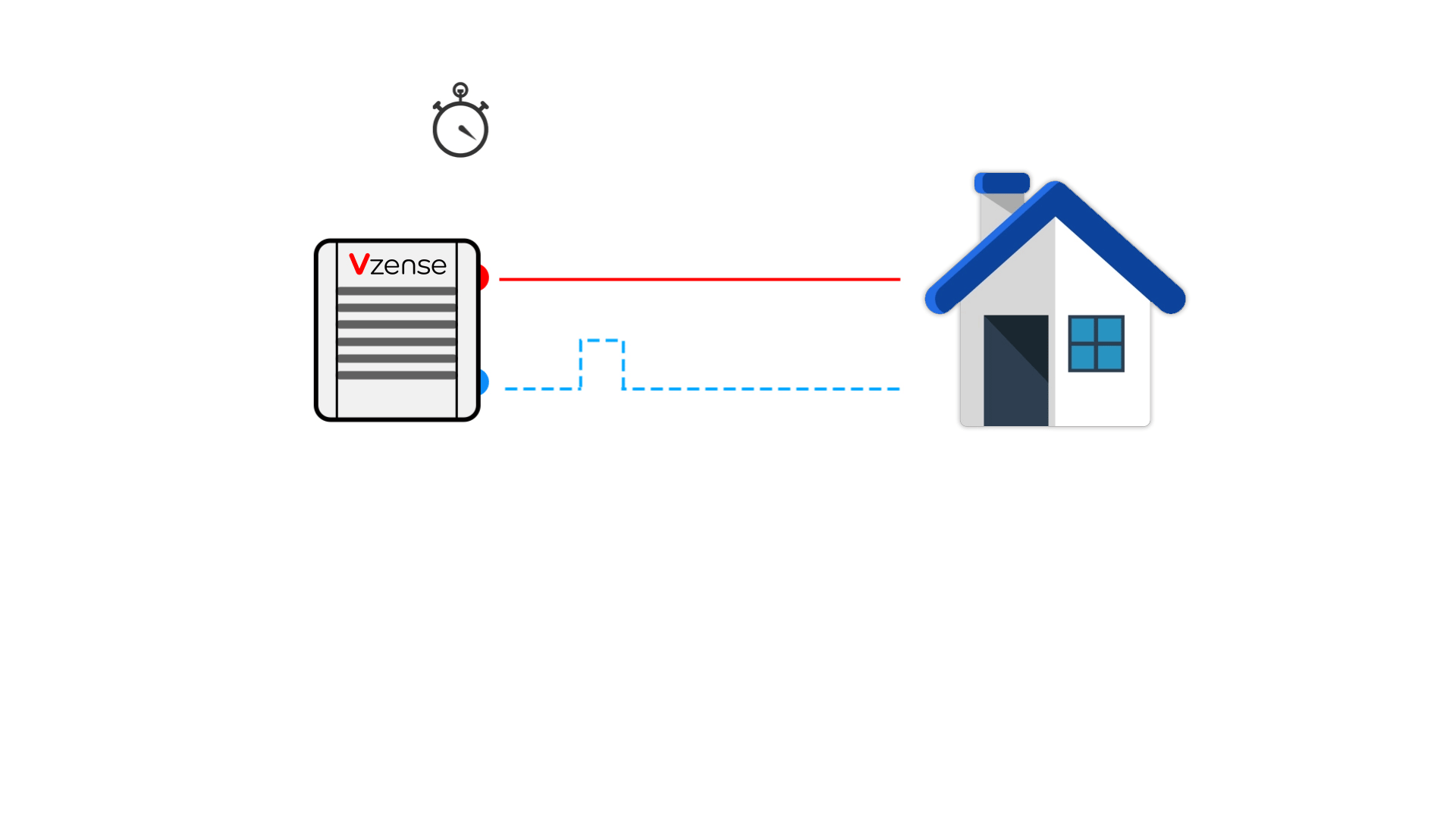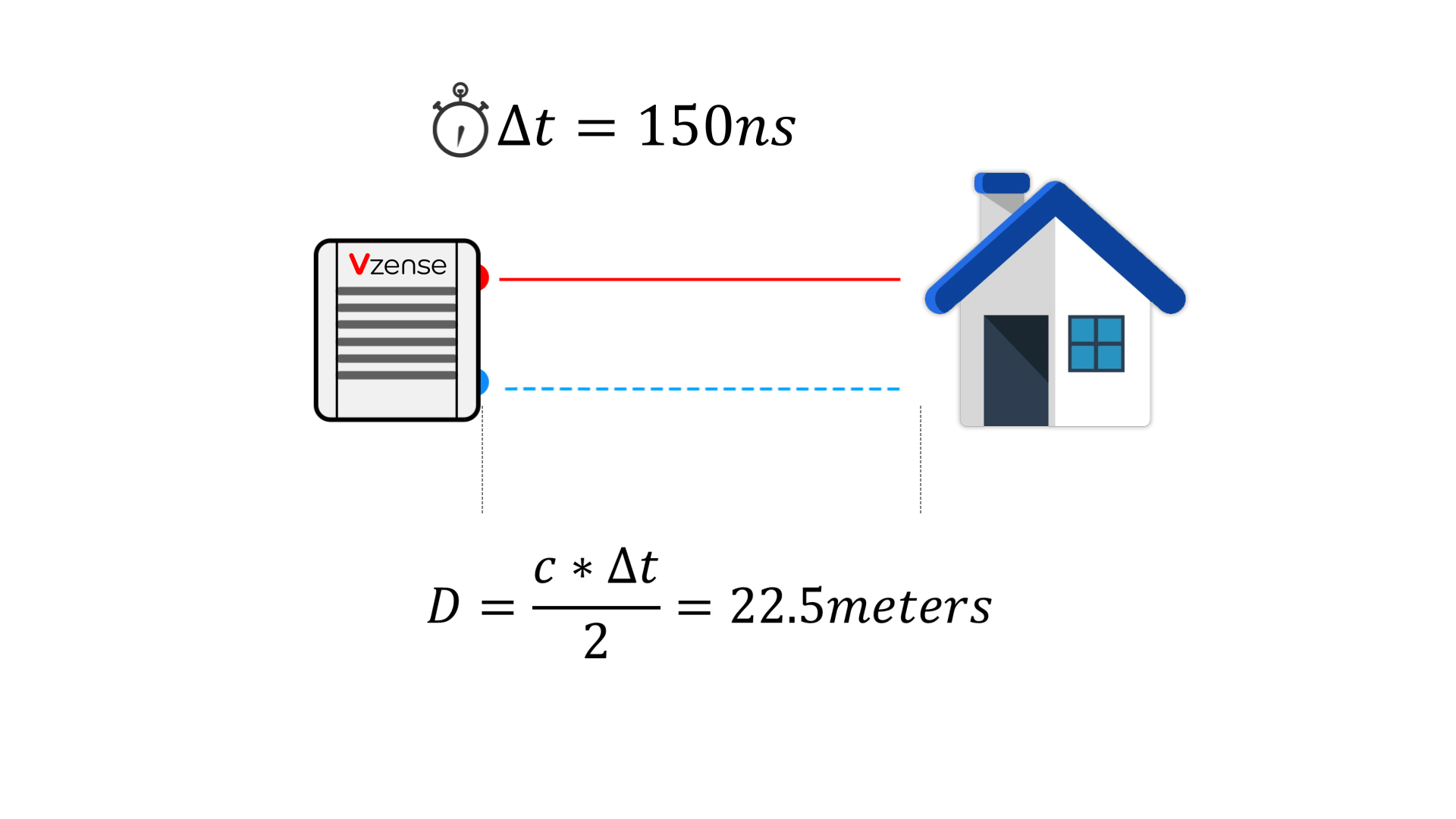
2. Indirect Time of Flight (iToF)
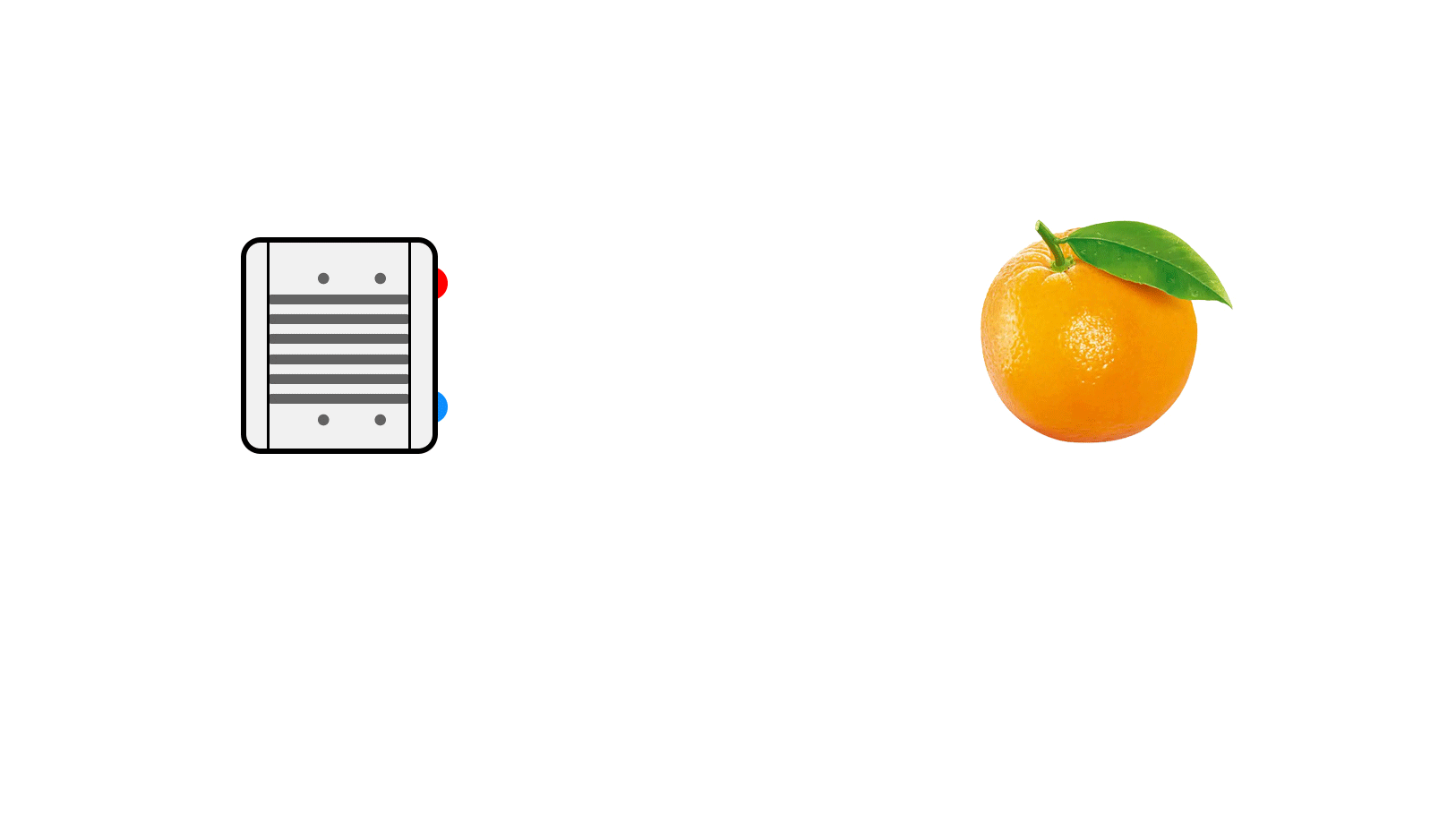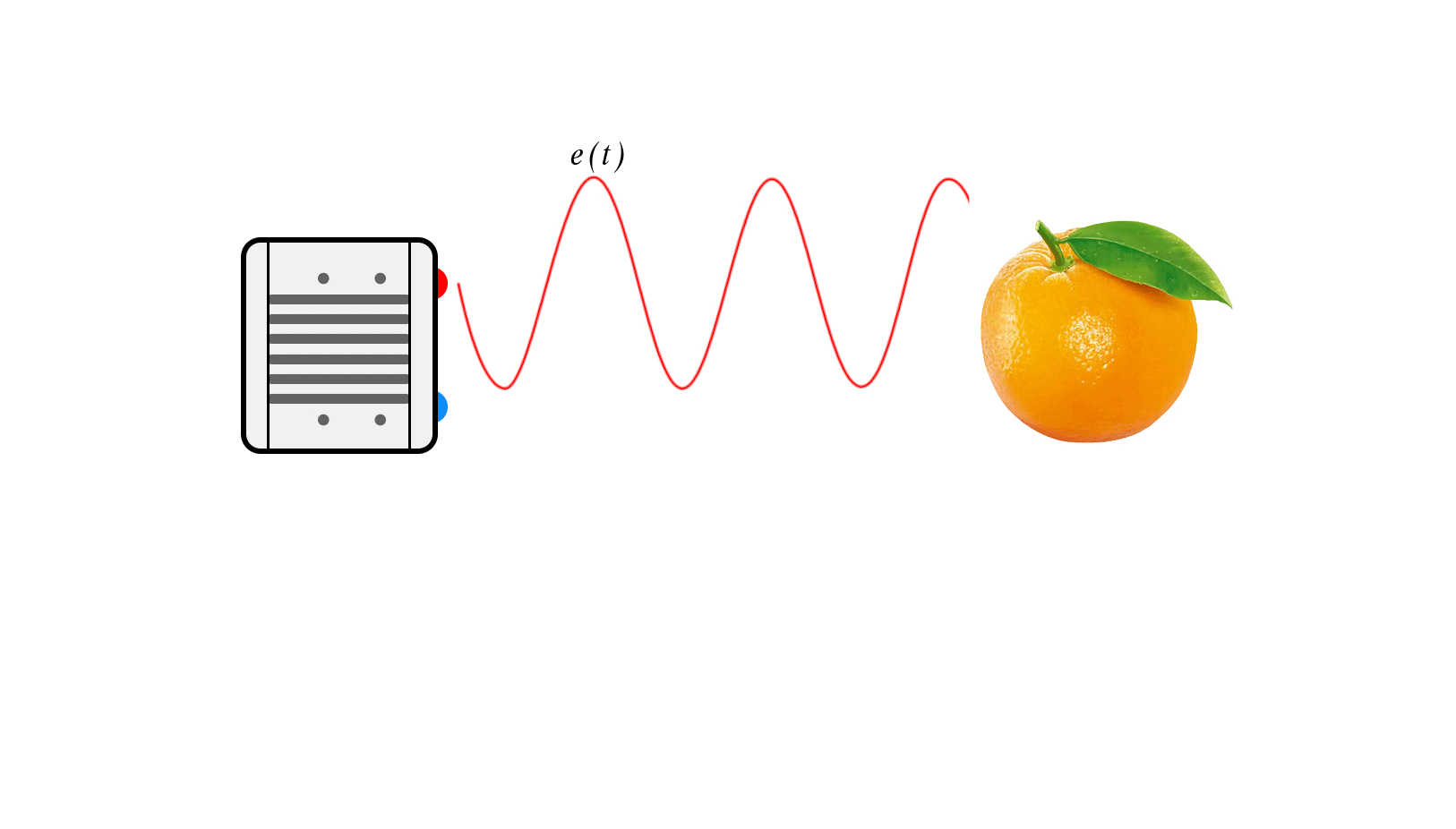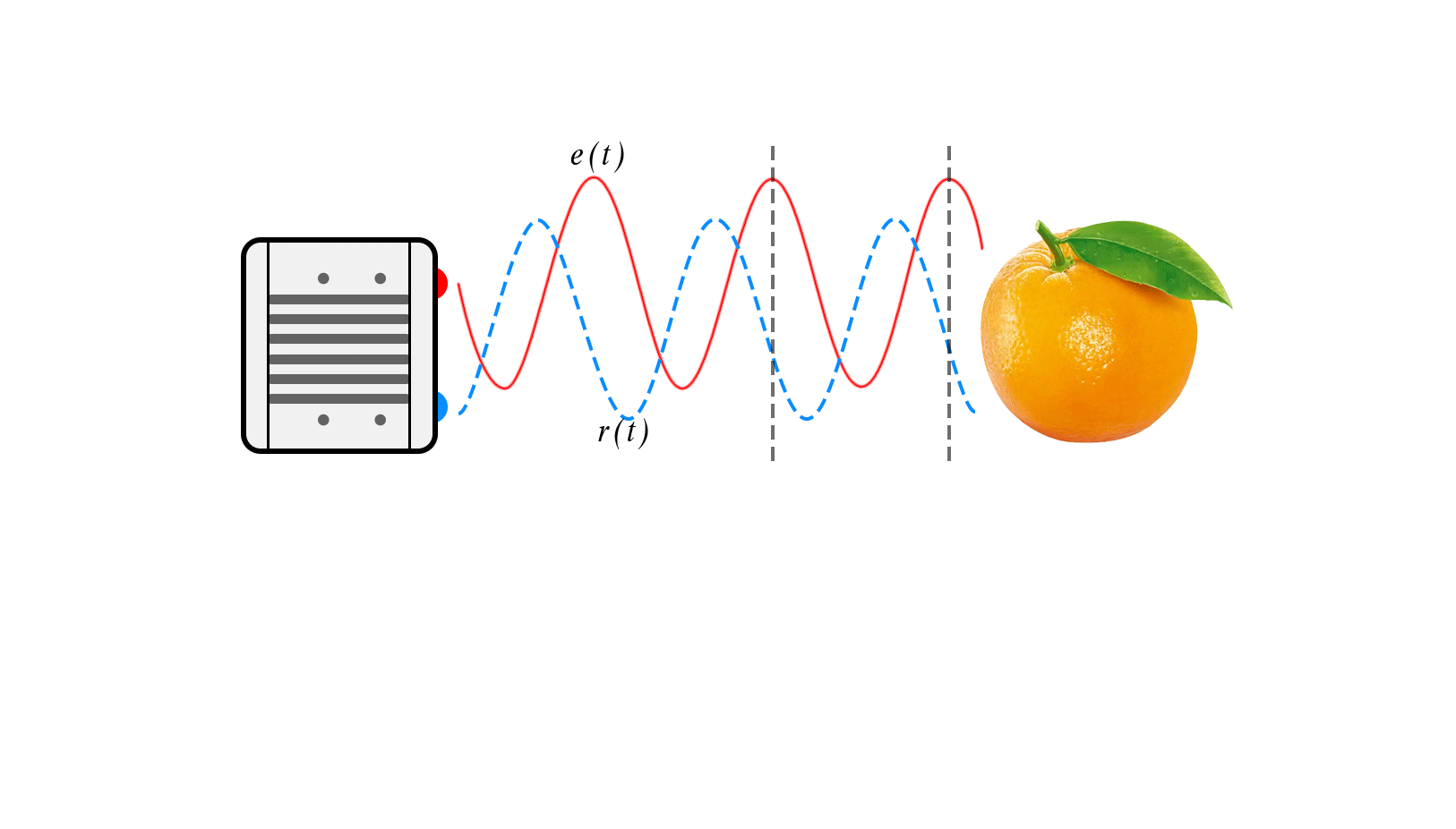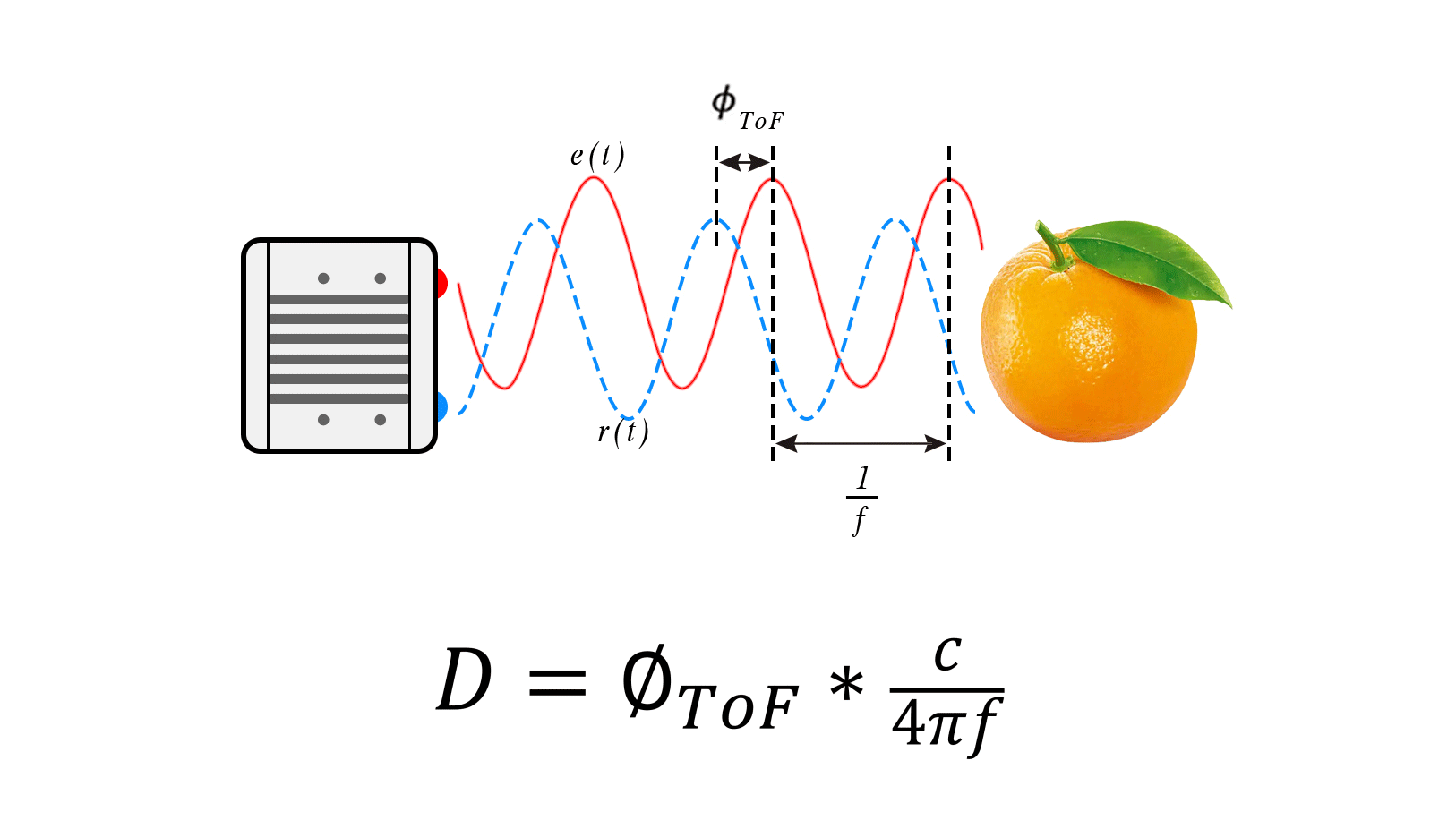
Principle: It calculates distance by actively emitting modulated light to illuminate the target, receiving the reflected light signal, and measuring the phase difference to determine time.
Types: Continuous Wave indirect Time-of-Flight (CW-iToF) technology and Pulse indirect Time-of-Flight (P-iToF) technology.
System architecture
1. LiDAR
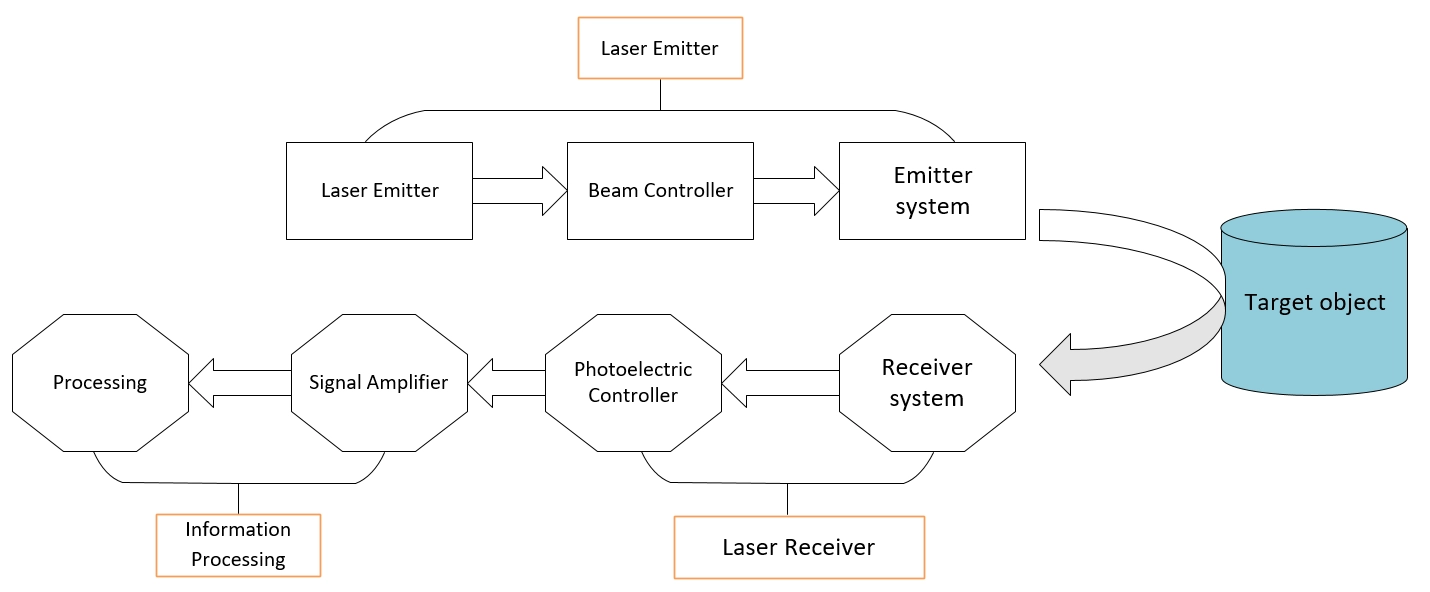
Structural Components: LiDAR consists of four main systems: laser emission, laser reception, beam manipulation, and information processing, as shown in the diagram below:
Active scanning: Relies on a mechanical scanning structure to detect point by point or line by line, as shown in the diagram below:
Based on the different beam scanning methods, LiDAR can be classified into mechanical LiDAR, semi-solid-state LiDAR, and solid-state LiDAR, as shown in the table below:
| Type | Technical Architecture |
|---|---|
| Mechanical LiDAR | Mechanical rotating |
| Semi-solid-state LiDAR | MEMS |
| Galvanometer | |
| Prisms | |
| Solid-state LiDAR | OPA |
| FLASH |
2. iToF Camera
Structural Components: iToF camera refers to a planar non-scanning 3D imaging depth information capture technology that uses an optical system as the receiving pathway. It mainly consists of components such as an illumination unit, optical lens, imaging sensor, control unit, and computing unit, , as shown in the table below:
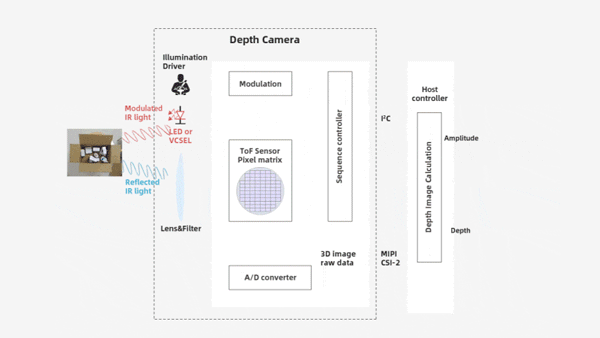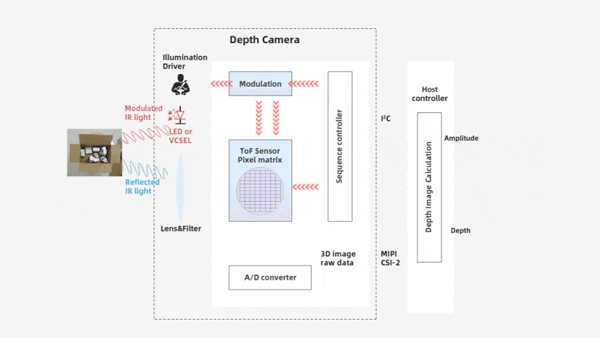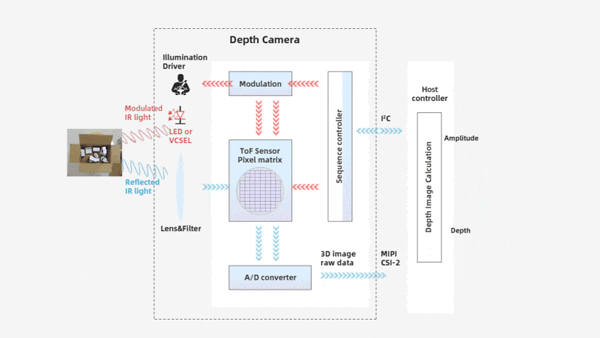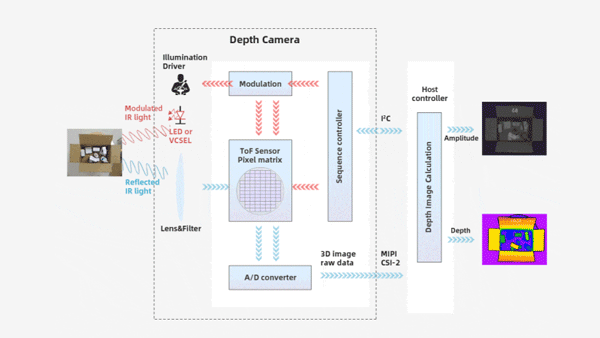
Planar array detection: Captures the depth of the entire scene in a single exposure (no scanning required), operating independently, as shown in the table below:
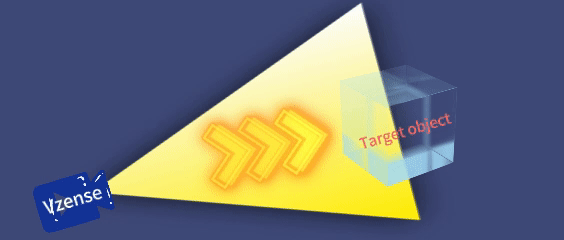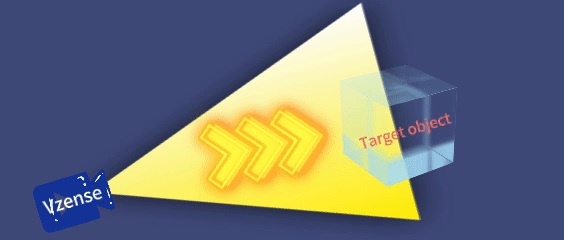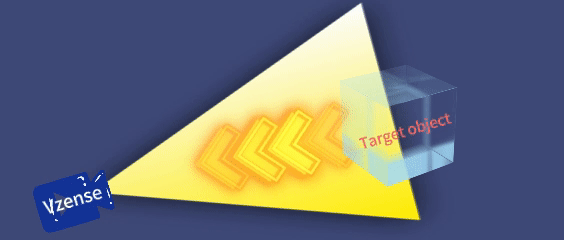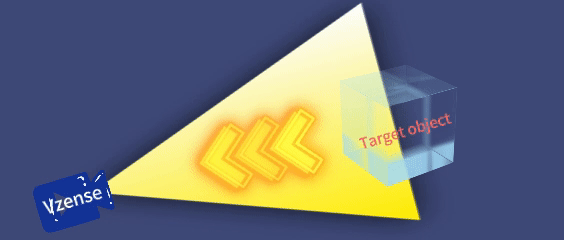
Based on the differences in emitted light signals, iToF cameras are classified into DS series cameras, which are based on continuous wave technology, and NYX series cameras, which are based on pulse technology. The specific models are listed in the table below:
| Type | Technical architecture |
|---|---|
| DS series(CW-iToF) | DS86 |
| DS87 | |
| DS77 Lite/Pro | |
| DS77C Lite/Pro | |
| NYX series(P-iToF) | NYX650 |
| NYX660 | |
| NYX650S |
Core performance comparison
| Type | LiDAR | iToF camera |
| Detection range | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
| Accuracy and precision | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Environment interference | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Power consumption | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
Comparison of advantages and disadvantages
1. LiDAR
Pros: Strong capability for long-distance detection; suitable for high-speed motion scenarios (e.g., autonomous driving); high adaptability to various environments.
Cons: Expensive; large size and limited lifespan of mechanical LiDAR (due to wear on rotating components); complex data processing (point clouds require GPUs or specialized chips for analysis); difficulty in rapid object recognition and localization.
2. iToF Camera
Pros: Low cost, low power consumption, compact size, and easy integration; strong real-time performance (high frame rate) with detailed target features; excellent object recognition capabilities for fast segmentation and localization.
Cons: Accuracy affected by multipath reflection and ambient light noise; short detection range with poor long-distance performance; high requirements for object reflectivity, making it difficult to detect transparent or highly reflective surfaces.
Application scenarios
1. LiDAR
Autonomous driving: Used for high-precision environmental perception (e.g., Waymo, Level 4 vehicles).
Industrial measurement: 3D modeling, bridge inspection, and geological exploration.
Robot navigation: Obstacle avoidance and path planning for AGVs and warehouse robots.
Smart Cities: Traffic flow monitoring and building digitization.
2. iToF Camera
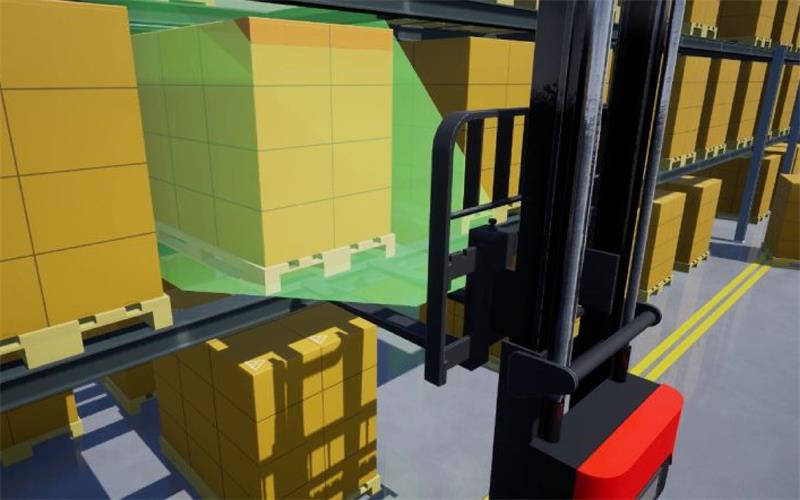
Industrial robot identification: Pallet recognition and obstacle avoidance for AGVs and AMRs.
Smart depalletizing: Dynamic grasping and sorting.
Logistics field: Single-item separation and warehouse slot detection.
Security monitoring: Passenger flow counting and restricted area intrusion detection.
Smart agriculture: Recognition and picking of fruits and vegetables.