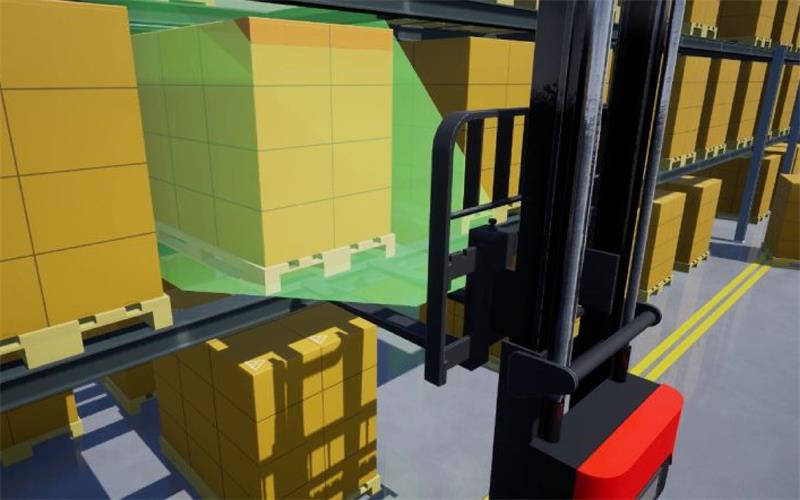
When an autonomous forklift precisely lifts a barcode-labeled carton, or when a robotic arm (nicknamed the “spider hand”) skillfully grabs components of the same color — What makes this level of precision possible?
The secret lies in a powerful piece of technology: the RGB-D camera.
This isn’t just a camera — it’s the robot’s eyes, and in some ways, even part of its brain. Today, let’s take a closer look and break down the “black technology” behind it.
Table of Contents
What is an RGB-D Camera?
Let’s start by breaking down its name to understand its meaning.
The Meaning Behind “RGB-D”
- RGB refers to an RGB camera, also known as a color camera—essentially what we commonly think of as a standard camera. The images it captures display an object’s shape and color.
- The term “RGB” comes from its ability to detect Red, Green, and Blue light—the three primary color channels that human cone cells are most sensitive to. By combining these, the camera can reproduce most colors visible to the human eye.
- D stands for Depth camera, which measures the distance (depth) between objects and the camera. Different types of depth sensors use various techniques to generate point clouds or depth maps, where each point contains precise depth information.
How Does an RGB-D Camera Work?
An RGB-D camera integrates both RGB and depth sensors in hardware. Through algorithms (typically rigid alignment), it combines:
- RGB images (capturing color and texture)
- Depth maps (providing 3D spatial data)
The result is a single output that contains both color and depth, enabling machines to perceive the world in 3D with full visual context.
Why Do We Need RGB-D Cameras?
Recent advancements in 3D vision technology—including improved accuracy, extended range, and better low-light performance—have driven a surge in demand for depth sensing.
By fusing RGB color data with depth information, RGB-D cameras significantly enhance:
✔ Object recognition & detection accuracy
✔ Robotic grasping & manipulation (e.g., robotic arms)
✔ Autonomous navigation (e.g., mobile robots)
✔ Logistics automation (e.g., pallet & cargo identification)
✔ Healthcare monitoring (e.g., remote patient tracking)
A Key Advantage: Reducing Computational Load
Consider this example: (See more details in the article :The using and setting of RGB sensor in Vzense 3D camera)
- In an RGB image, a white target object blends into a similarly colored background, making detection computationally expensive.
- The depth map, however, clearly distinguishes foreground objects (within working range) from the distant background.
- The RGB-D fusion allows precise object segmentation, cutting unnecessary background processing and drastically reducing computational overhead.
Our RGB-D Camera Solution
Goertek’s 3D Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras come in two flagship series:
- Continuous-Wave iToF DS Series
- Pulsed-Wave iToF NXY Series
Both feature global shutter RGB-D imaging, delivering high-precision depth sensing for industrial and commercial applications.
Stay Updated!
Want to learn more about ToF technology and products? Subscribe to our website for the latest insights.
Until next time!